Guideline For Secure Hosting
Securing your hosting environment in 2024 is crucial to safeguarding your website and sensitive data from evolving cyber threats. Begin by choosing a reputable hosting provider that prioritizes security measures, such as encryption protocols, regular security audits, and robust firewalls.
Opt for a hosting plan that aligns with your website’s needs, ensuring sufficient resources to handle traffic while maintaining optimal security. Keep all software, including the operating system, web server, and applications, up-to-date with the latest security patches.
Implement a strong password policy and enable two-factor authentication to add an extra layer of protection. Regularly backup your data and store it in a secure offsite location to mitigate the impact of potential breaches.
Utilize a web application firewall (WAF) to filter and monitor HTTP traffic, protecting against common web application attacks. Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential weaknesses in your hosting environment.
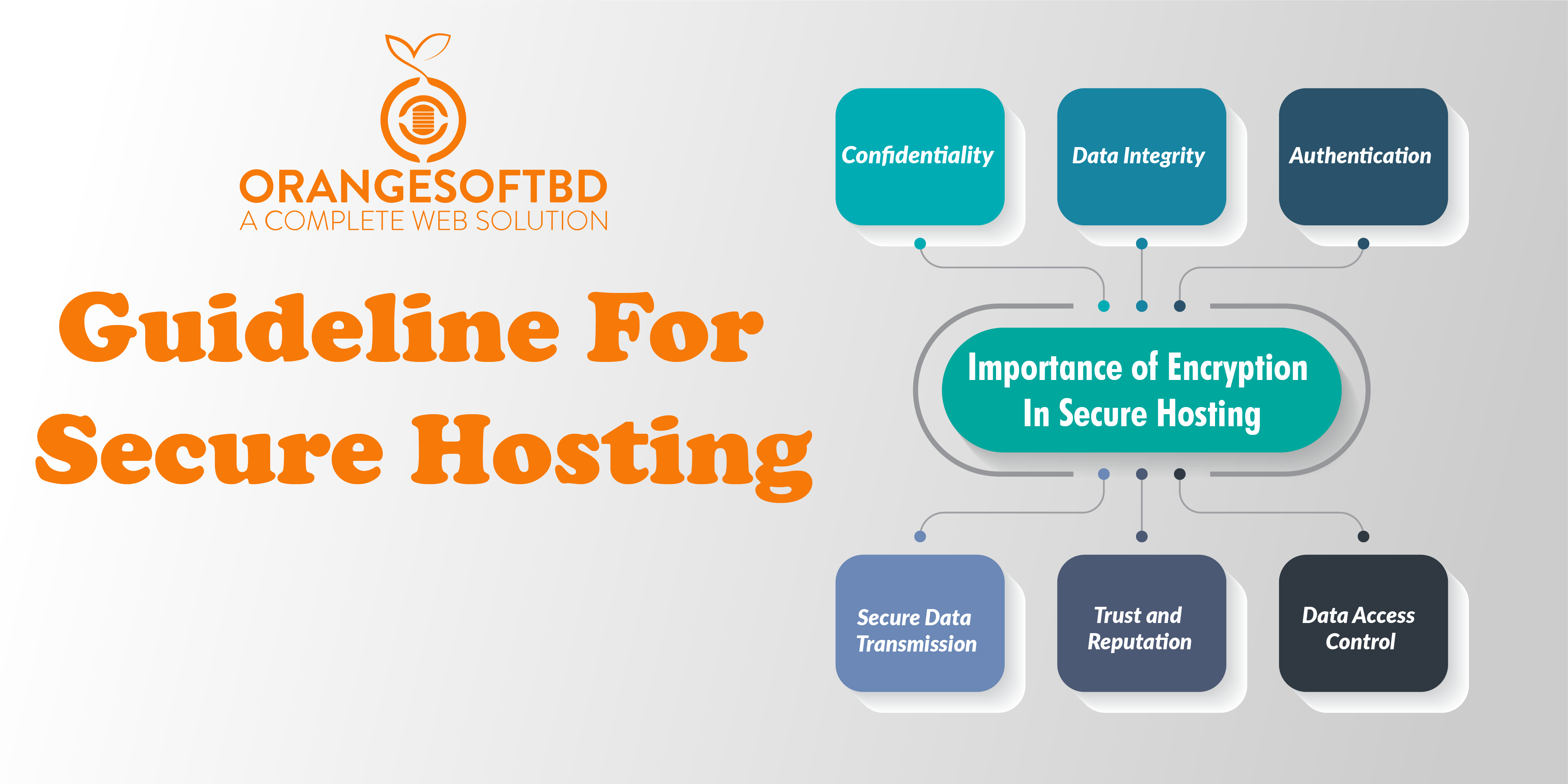
Importance of Encryption in Secure Hosting
Encryption plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and privacy of data in various online environments, including secure hosting. Here are some key reasons highlighting the importance of encryption in secure hosting:
Confidentiality:
Encryption protects sensitive information from unauthorized access by converting it into a format that is unreadable without the proper decryption key. In a secure hosting environment, this ensures the confidentiality of data stored on servers.
Data Integrity:
Encryption helps maintain the integrity of data by detecting any unauthorized modifications or tampering. With encryption in place, even if an attacker gains access to the data, they cannot alter it without the proper decryption key.
Authentication:
Encryption supports authentication mechanisms, ensuring that communication between servers and clients is secure and that parties can verify each other’s identities. This helps prevent man-in-the-middle attacks and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Secure Data Transmission:
Encryption ensures that data transmitted between clients and servers is secure, preventing eavesdropping and interception. This is particularly important for sensitive transactions, such as online banking, e-commerce, or any other platform dealing with personal or financial information.
Trust and Reputation:
Implementing strong encryption measures in secure hosting helps build trust with users and clients. Customers are more likely to use a service or website that prioritizes the security of their data, and a positive reputation for security can be a competitive advantage.
Data Access Control:
Encryption is an essential component in controlling access to data. Even if someone gains access to the server, they won’t be able to access sensitive information without the appropriate encryption keys, limiting the potential damage in case of a security breach.
Encryption is a fundamental aspect of secure hosting, providing a multi-faceted defense against unauthorized access, data breaches, and various cyber threats. It is a critical component in maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and trustworthiness of data in online environments.
Best Practices for Secure Server Configurations
Securing server configurations is crucial to ensure the overall security of a system. Here are some best practices for secure server configurations:
- Minimalist Installation:
Install only the necessary components and services required for the server’s functionality. Remove or disable any unnecessary services and applications to minimize the potential attack surface.
- Regular Updates and Patching:
Keep the operating system, server software, and all installed applications up-to-date with the latest security patches. Regularly apply updates to address known vulnerabilities and improve overall system security.
- Strong Authentication:
Enforce strong password policies, use multi-factor authentication (MFA) where possible, and disable unnecessary accounts. Limit the number of users with administrative privileges and use unique, complex passwords.
- Firewall Configuration:
Configure and maintain a firewall to control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Only allow necessary services and ports to be accessible, and regularly review and update firewall rules based on changing security requirements.
- Secure Communication Protocols:
Use secure communication protocols such as TLS (Transport Layer Security) for data in transit. Disable outdated and insecure protocols like SSL. Ensure proper configuration of encryption ciphers and algorithms.
Regular Security Audits and Scans:
Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability scans to identify and address potential security weaknesses. Automated tools and manual reviews can help ensure the ongoing security of the server.
File System Security:
Implement proper file and directory permissions. Restrict access to sensitive files and directories to only authorized users. Regularly review and audit file permissions to detect any unauthorized changes.
Secure Server Hardening:
Follow industry best practices for server hardening, which may include disabling unnecessary services, removing default accounts, and configuring security settings to reduce the server’s exposure to potential threats.
Regular Backups:
Implement regular backup procedures to ensure that critical data can be recovered in the event of a security incident or system failure. Test backups periodically to ensure their integrity and reliability.
Incident Response Plan:
Develop and maintain an incident response plan outlining the steps to be taken in case of a security breach. This plan should include procedures for identifying, containing, eradicating, recovering, and learning from security incidents.
By following these best practices, organizations can significantly enhance the security of their server configurations and mitigate the risks associated with potential security threats and vulnerabilities.
The Role of Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) play critical roles in enhancing network security by monitoring and controlling network traffic. They serve distinct but complementary functions in protecting systems and data from unauthorized access, malicious activities, and potential security threats.
Firewalls:
Access Control:
Firewalls act as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet. They control and filter incoming and outgoing traffic based on a set of predetermined security rules.
Packet Filtering:
Firewalls inspect packets of data and make decisions to allow or block traffic based on predefined rules. This helps prevent unauthorized access, denial-of-service attacks, and other network-based threats.
Stateful Inspection:
Modern firewalls often employ stateful inspection, which keeps track of the state of active connections and makes decisions based on the context of the traffic. This enhances security by understanding the state of a communication session.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS):
Real-Time Monitoring:
IDS continuously monitor network and system activities in real time. They analyze traffic patterns, behavior, and anomalies to detect potential security incidents or abnormal activities.
Signature-Based Detection:
IDS use signature-based detection to identify known patterns of attacks by comparing network traffic against a database of predefined attack signatures. This method is effective for recognizing well-known attack patterns.
Behavioral Analysis:
IDS employ behavioral analysis to identify deviations from normal network behavior. Unusual patterns, such as sudden spikes in traffic or abnormal access patterns, can trigger alerts.
Anomaly Detection:
Anomaly detection involves establishing a baseline of normal behavior and triggering alerts when deviations occur. This method is effective for detecting previously unknown threats or zero-day attacks.
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems are essential components of a comprehensive security strategy, providing protection at different layers of the network and helping organizations defend against a wide range of cyber threats.
Proactive Measures to Detect and Mitigate Security Incidents
Detecting and mitigating security incidents in a proactive manner is crucial for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of data. Here are proactive measures to help organizations identify and respond to security incidents effectively:
- Continuous Monitoring:
Implement continuous monitoring of network and system activities. This involves real-time analysis of logs and system behavior to identify anomalies or suspicious patterns that could indicate a security incident.
- Security Information and Event Management:
Deploy SIEM systems to aggregate, correlate, and analyze logs and events from various sources. SIEM tools provide a centralized platform for monitoring and responding to security incidents.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics:
Use UEBA solutions to analyze user behavior and detect anomalies. This helps identify potential insider threats or compromised user accounts by understanding normal patterns of activity.
- Threat Intelligence Integration:
Integrate threat intelligence feeds into security systems to stay informed about emerging threats and known attack patterns. This enables proactive identification of potential risks before they manifest into security incidents.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing:
Conduct regular vulnerability scans and penetration tests to identify weaknesses in systems and applications. Addressing vulnerabilities before they are exploited can prevent security incidents.
By implementing these proactive measures, organizations can significantly enhance their ability to detect and mitigate security incidents before they escalate. A comprehensive and well-integrated approach to security is essential for effectively managing and responding to the evolving threat landscape.
Assessing Risks and Ensuring Security in Cloud Environments
Assessing risks and ensuring security in cloud environments is crucial due to the sensitive nature of data and applications hosted in the cloud. Cloud security involves protecting data, applications, and infrastructure in the cloud from various threats. Here are key considerations and best practices for assessing risks and ensuring security in cloud environments:
- Data Encryption:
Implement encryption for data in transit and at rest to protect sensitive information.
Use strong encryption algorithms and ensure proper key management practices.
- Identity & Access Management :
Implement strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Regularly review and update access controls to ensure that only authorized users have access to resources.
- Network Security:
Utilize Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and network security groups to control traffic flow and restrict access to resources.
Implement firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems to monitor and block malicious activity.
- Regulatory Requirements:
Understand and adhere to industry-specific compliance standards and regulatory requirements.
Regularly audit and assess the cloud environment to ensure compliance with applicable standards.
- Data Backups:
Regularly back up critical data and ensure that disaster recovery plans are in place.
Test the recovery process to ensure data integrity and minimal downtime in case of a disaster.
- Vendor Security:
Evaluate the security measures implemented by the cloud service provider (CSP).
Understand the shared responsibility model and clarify security responsibilities between the CSP and the customer.
By incorporating these practices into your cloud security strategy, you can help mitigate risks and ensure a secure environment for your data and applications in the cloud. Regularly reassessing and updating security measures is crucial in the dynamic landscape of cybersecurity.
Tips For of Secure host Employee Training
Securing employee training sessions is essential to protect sensitive information and ensure that participants can focus on learning without concerns about potential security risks. Here are tips for securely hosting employee training sessions:
- Use Secure Platforms:
Choose a secure and reputable platform for hosting virtual training sessions. Ensure that the platform complies with industry security standards.
- Encrypted Communication:
Ensure that all communications, including video, audio, and data transfers, are encrypted to protect against eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
- Session Encryption:
If the training platform supports end-to-end encryption, enable it to secure the content of the training sessions.
- Secure File Sharing:
If training materials or documents need to be shared, use secure file-sharing mechanisms with proper access controls and encryption.
- Monitor Participants:
Regularly monitor the list of participants during the training session to detect and address any unauthorized attendees.
- Customized Permissions:
Grant participants only the necessary permissions required for the training session to minimize potential security risks.
By incorporating these tips into your approach to hosting employee training, you can enhance the security of the sessions and create a safer learning environment for your team. Regularly review and update security measures to adapt to evolving threats and technologies.
Conclusion
Securing employee training sessions is a critical aspect of safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring a productive and secure learning environment. By adopting a comprehensive approach to security, organizations can mitigate potential risks associated with virtual training.
By integrating these best practices into the hosting of employee training, organizations can enhance the overall security posture of their virtual learning initiatives, fostering a safe and conducive environment for professional development.
Regular updates, continuous monitoring, and adaptability to emerging security challenges are essential for maintaining a robust security framework in the dynamic landscape of virtual training.